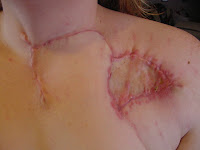
When the skin is damaged through an abrasion, nick, or cut our body's natural response is to form new tissue, sometimes leading to scarring which is typically flat, well-approximated and shiny. However, during the formation of scar tissue, if the body over compensates during the healing process, an abnormally large scar is formed that extends the original border of the injured site resulting in a keloid scar. The keloid, or keloid scar may appear shiny, pink, purple, and sometimes white in color. Keloid scar have irregular patterns, may be dome shaped or elongated and may progressively enlarge over time. In contrast to hypertropic scar which do not extend the borders of the original injury, keloid scar surpass the the site and cause the suffered to experience a disturbed body image and embarrassment. They often cause discomfort, becoming itchy and sometimes painful.
The most common areas of the body for keloid scar formation are the shoulders, chest, and earlobes. They may however be found on other areas of the body.
Keloid scar may form after any injury to the skin. Any cut, scrape, or puncture of the skin has the potential to form keloid scar in those who are prone to keloid formation. Many keloid will form due to ear piercing, resulting in unsightly keloid on the earlobe. Acne is another well-known source for keloid formation. Those with acne may form keloid on the shoulder and chest area due the overgrowth of acne scar. Any surgical site has the potential of forming a keloid. Some women have suffered from keloid scar formation following c-sections.
For those who suffer from keloid scar formation, prevention is key. Keloid scar form from the overgrowth of collagen, scar tissue at the site of injury. Unfortunately, it is difficult to prevent such injuries to the skin. If a cut, scrape, burn, or puncture occurs it is important to cleanse the wound with mild soap and water and treat triple antibiotic ointment or other antibacterial/antibiotic ointment. The site should be compressed in the form of a bandage or other compression to aid in the prevention of a keloid scar forming. This treatment should be continued until the injury is completely healed. If a keloid begins to form, it is important to begin treating the scar immediately. Treatment is much more effective in the early stages of keloid growth.
Most Affected by Keloid Scar
There is evidence that sufferers of keloid scar have a genetic tendency. Men and women seem to be of equal prevalence, however those with darker skin tones seem to be affected at a higher rate. The elderly and children are less effected by keloid.Areas of the Body Form Keloid Scar
The most common areas of the body for keloid scar formation are the shoulders, chest, and earlobes. They may however be found on other areas of the body.
Causes Keloid Scar
Keloid scar may form after any injury to the skin. Any cut, scrape, or puncture of the skin has the potential to form keloid scar in those who are prone to keloid formation. Many keloid will form due to ear piercing, resulting in unsightly keloid on the earlobe. Acne is another well-known source for keloid formation. Those with acne may form keloid on the shoulder and chest area due the overgrowth of acne scar. Any surgical site has the potential of forming a keloid. Some women have suffered from keloid scar formation following c-sections.
Prevent Keloid Scar
For those who suffer from keloid scar formation, prevention is key. Keloid scar form from the overgrowth of collagen, scar tissue at the site of injury. Unfortunately, it is difficult to prevent such injuries to the skin. If a cut, scrape, burn, or puncture occurs it is important to cleanse the wound with mild soap and water and treat triple antibiotic ointment or other antibacterial/antibiotic ointment. The site should be compressed in the form of a bandage or other compression to aid in the prevention of a keloid scar forming. This treatment should be continued until the injury is completely healed. If a keloid begins to form, it is important to begin treating the scar immediately. Treatment is much more effective in the early stages of keloid growth.
Those who are prone to keloid should avoid:
- Ear Piercing- This is a common site for keloid growth. If you have a history of keloid scar the puncturing of the ear lobe is likely to form a keloid nodule.
- Elective Surgery- Surgical incisions are to be avoided unless medically necessary.
- Shaving- Be cautious when shaving if you are prone to keloid. Opt for using an electric razor or other means of hair removal.
- Acne- Acne is another major source for keloid formation. Those with acne have the potential for forming numerous keloid, especially on the chest and shoulder areas. Be of care not to "pop" pimples. Prevention of acne is key, see your health provider for information and treatment options.
read also Keloid Removing Cost





{ 0 comments... Views All / Send Comment! }
Post a Comment